What to do if you have a sudden hearing loss?
How does an ear infection affect hearing and what can I do if I lose my hearing after a sudden hearing loss?
 Under sudden deafness is a sudden onset of sensorineural hearing loss without an identifiable cause.
Under sudden deafness is a sudden onset of sensorineural hearing loss without an identifiable cause.
Some sufferers describe the sensation of hearing through absorbent cotton after a sudden hearing loss. Others do not perceive the reduction in volume as such, but rather a change in the sound image or that the localization of sound sources and understanding background noise suddenly becomes difficult or even impossible. The cause is a hearing loss in several neighboring frequencies of around 30 decibels - rarely even more, up to 70 decibels - which often only occurs on one side.
Unpleasant accompanying symptoms can be tinnitus in the affected ear, and rarely also dizziness.
The symptoms often subside within a few weeks. With one exception: if the sudden hearing loss was caused by an occlusion of the blood vessels that supply the inner ear with oxygen, the hearing loss may not be reversible. In the case of sudden hearing loss in the broader sense, however, further episodes may occur.
Hearing care for sudden hearing loss
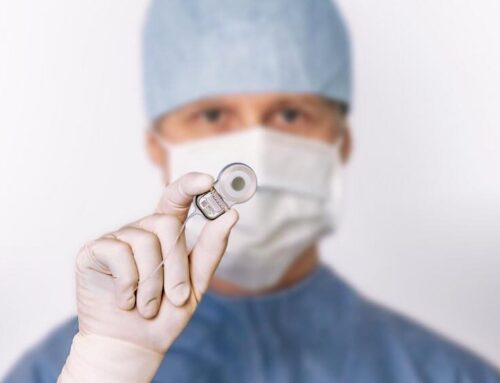
If the hearing loss remains permanent after a sudden hearing loss, a hearing aid or hearing implant can help. This should also be considered if hearing is only affected on one side: understanding speech in noise is very difficult or even impossible with only one ear; localizing a sound source is also much easier with hearing on both sides.

You are currently reading: